Book on Whatsapp
9892101616
PCOS Decoded: Understanding and Managing Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
PCOD / PCOS
Sat Jul 08 2023
Introduction: Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women worldwide. If you've been diagnosed with PCOS or suspect you may have it, understanding the importance of testing and management strategies is crucial for your overall well-being. This blog aims to provide you with valuable insights into PCOD, including the essential tests for diagnosis and effective management strategies to lead a healthier life.
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome - is a common hormonal disorder that impacts the reproductive system in women. It is characterized by the presence of numerous small cysts on the ovaries, irregular menstrual cycles, and hormonal imbalances. This article provides an in-depth understanding of PCOD, including its signs and symptoms, underlying causes, associated risk factors, and the crucial significance of early detection and diagnosis..
Definition and Overview of PCOD
PCOD is an endocrine disorder that impacts the reproductive health of women. It is characterized by the presence of enlarged ovaries with multiple small cysts, which disrupt the normal ovulation process. This hormonal imbalance can lead to various health complications, if left untreated.
Common Signs and Symptoms of PCOD
PCOS manifests differently in individuals, and being aware of the common signs and symptoms can aid in early detection and prompt medical intervention.
Some typical manifestations of PCOS include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Women with PCOS may experience infrequent, prolonged, or absent periods due to the disruption of ovulation.
- Excessive hair growth (hirsutism): PCOS can cause abnormal hair growth, such as facial hair, as well as excess hair on the chest, back, and abdomen.
- Acne: Persistent acne can develop on the face, chest, and upper back due to hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS.
- Weight gain: Women with PCOS may struggle with weight management, experiencing difficulties in losing weight or experiencing sudden weight gain.
- Insulin resistance: PCOS can contribute to insulin resistance, resulting in high levels of insulin and problems with blood sugar regulation.
- Hair thinning or hair loss (alopecia): PCOS can lead to hair thinning or patches of baldness, affecting the scalp and other areas.
- Darkening of the skin: A condition called acanthosis nigricans may occur, characterized by dark patches of skin on the neck, groin, and under the breasts. It is associated with insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances in PCOS.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of PCOD is unknown, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone disrupt the normal balance of female hormones.
- Insulin Resistance: The body's cells become resistant to the action of insulin, leading to increased insulin production. This can further exacerbate hormone imbalances.
- Genetics: PCOD tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the body can contribute to the development of PCOD.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and stress can increase the risk of PCOD.
Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis:
Early detection and diagnosis of PCOD are crucial for several reasons:
- Treatment and Management: Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and management of symptoms, reducing the risk of long-term complications.
- Fertility Concerns: PCOD can impact fertility, and early diagnosis enables women to explore fertility treatment options if desired.
- Metabolic Health: PCOD is associated with an increased risk of metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Early detection helps in implementing preventive measures and managing these risks.
- Emotional Well-being: PCOD can have a significant impact on emotional well-being. Early diagnosis allows for early psychological support and counselling.
Diagnostic Tests for PCOD
- Blood tests: Hormone levels (LH, FSH, Testosterone, etc.), Fasting Glucose, Lipid Profile
- Ultrasound imaging: Evaluating ovarian cysts, uterine lining thickness
- Other potential tests: Glucose tolerance test, insulin levels, Thyroid Function Test
Effective Management Strategies for PCOS
A. Lifestyle Changes
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in managing PCOS. It can help regulate hormonal imbalances and improve symptoms.
- Dietary Recommendations: Adopting a healthy eating plan that includes balanced meals, portion control, and nutrient-rich foods can support PCOS management. Opt for lean proteins, whole grains, healthy fats, fruits and vegetables.
- Regular Physical Activity and Exercise: Engaging in regular aerobic exercise, strength training, and activities like yoga can improve insulin sensitivity, promote weight loss, and alleviate PCOS symptoms.
- Stress Management Strategies: Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, and relaxation exercises can help manage stress levels, which in turn can improve hormonal balance.
B. Medications and Hormonal Therapy
- Oral Contraceptives: These can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and manage symptoms such as acne and excessive hair growth.
- Anti-androgen Medications: These medications can reduce hair growth and improve acne by blocking the effects of male hormones (androgens).
- Insulin-Sensitizing Agents: Certain medications, such as metformin, can help manage insulin resistance and associated symptoms, such as weight gain and irregular periods.
C. Fertility Management
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): In cases where fertility is a concern, procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI) can assist in achieving pregnancy.
- Ovulation Induction: Medications may be prescribed to stimulate ovulation, increasing the chances of conception.
- Lifestyle Modifications to Enhance Fertility: Tracking menstrual cycles, identifying fertile periods, and making appropriate lifestyle adjustments can improve fertility outcomes.
D. Symptom-Specific Management
- Acne and Hirsutism Treatment: Various topical creams, oral medications, or hair removal techniques can help manage acne and excessive hair growth.
- Managing Irregular Periods: Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills or progesterone, can regulate menstrual cycles and promote regular periods.
- Psychological Support: Seeking counseling or support groups can provide emotional well-being and help cope with the challenges of PCOS.
Section 4: Long-Term Health Considerations
PCOS is associated with potential health risks such as insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Regular check-ups, health monitoring, and early intervention are vital to prevent and manage these risks effectively.
It is essential to adopt preventive measures, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and seek medical care when needed. By implementing these strategies, individuals with PCOS can lead healthier lives and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Conclusion:
Living with PCOD can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and management strategies, you can take control of your health and improve your quality of life. By undergoing appropriate diagnostic tests and implementing effective management techniques, you can manage PCOD symptoms, reduce potential health risks, and strive for a healthier future. Remember, consulting with a healthcare professional is vital for personalized guidance and support throughout your PCOD journey. If you suspect you have PCOD or experience any of the symptoms mentioned, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They can perform a comprehensive evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and specific tests to confirm the diagnosis and provide appropriate treatment and management strategies tailored to your needs.
Related Blogs
PCOD / PCOS
Impact of PCOS on Fertility and Women’s Health
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects millions of women during their reproductive years. Characterized by irregular periods, hormonal imbalance, and cysts in the ovaries, PCOS has far-reaching effects on fertility and overall health. Understanding its impact helps women manage symptoms and seek timely treatment.
PCOS and Fertility Challenges
One of the biggest concerns for women with PCOS is difficulty conceiving. The condition often leads to irregular ovulation or absence of ovulation, making natural conception challenging. Elevated levels of male hormones (androgens) further disrupt the reproductive cycle. However, with medical guidance, lifestyle changes, and fertility treatments, many women with PCOS can successfully become mothers.
Health Risks Beyond Fertility
PCOS is not just about fertility; it has broader health implications. Women with PCOS are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, obesity, and heart disease due to insulin resistance. Hormonal imbalance can also cause acne, excessive hair growth, and hair thinning, which affect self-esteem.
Emotional and Mental Health Impact
Living with PCOS can be emotionally draining. The constant struggle with weight, infertility, and appearance often leads to stress, anxiety, and depression. Emotional support, counseling, and self-care are essential components of a well-rounded treatment plan that supports confidence and overall well-being.
Managing PCOS Effectively
While PCOS cannot be fully cured, it can be managed effectively. Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, weight management, and a balanced diet rich in fiber and lean protein can significantly reduce symptoms. Medications and hormone therapies prescribed by doctors also help regulate cycles and improve fertility chances.
PCOS is a lifelong condition, but early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and medical treatment can help women lead healthier lives and improve their chances of conceiving. Addressing both physical and emotional aspects of PCOS ensures better outcomes and quality of life.
At Manipal TRUtest, our comprehensive PCOS and hormonal profile tests help detect imbalances early and guide the right treatment approach. With expert testing and accurate results, women can take charge of their health and move confidently toward a balanced, healthier future.
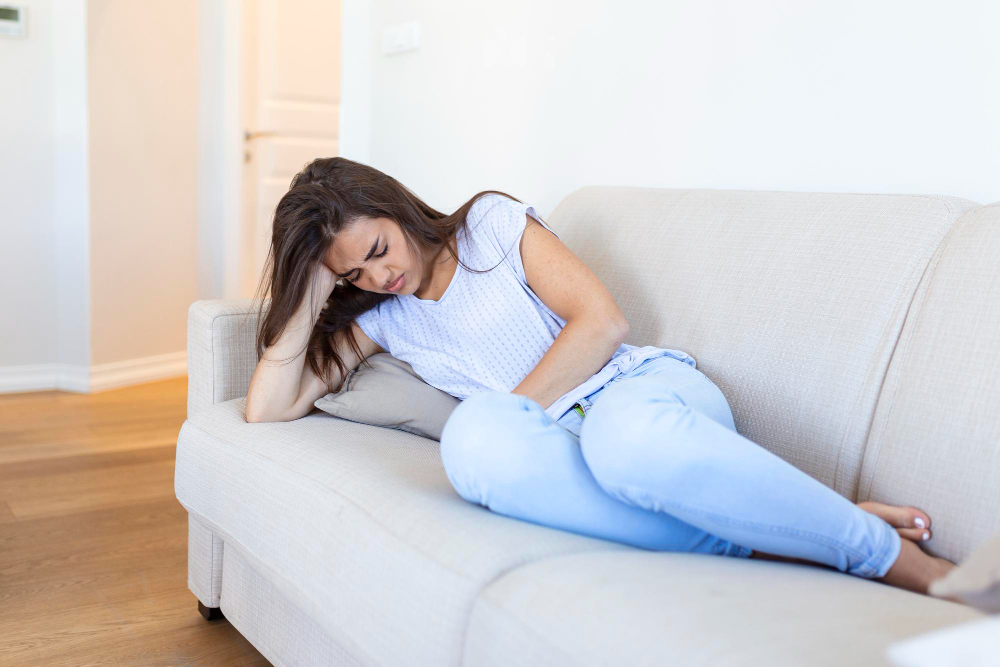

PCOD / PCOS
PCOD and Hormone Imbalance: What You Need to Know
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) is a common hormonal disorder that affects millions of women worldwide, particularly those of reproductive age. Characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, weight gain, acne, and infertility, PCOD arises from a complex interplay of hormonal imbalances that affect the ovaries and overall health. Understanding the connection between PCOD and hormone imbalance is crucial for early diagnosis, effective treatment, and long-term health management.
The Hormonal Imbalance Behind PCOD
Hormonal imbalance plays a central role in the development and progression of PCOD. The most common hormonal irregularities observed in PCOD include:
1. Increased Androgens (Male Hormones)
Women with PCOD often have higher levels of testosterone and other androgens, which can lead to:
- Excess facial and body hair (hirsutism)
- Severe acne
- Oily skin
- Scalp hair thinning or hair loss
2. Insulin Resistance
Many women with PCOD are resistant to insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. This means the body needs to produce more insulin to maintain normal glucose levels, which in turn stimulates the ovaries to produce more androgens.
Insulin resistance is a key contributor to:
- Weight gain, especially around the abdomen
- Increased risk of type 2 diabetes
- Difficulty in losing weight
3. Low Progesterone Levels
Low progesterone due to irregular ovulation can lead to:
- Irregular or missed periods
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Difficulty in maintaining pregnancy
Symptoms of PCOD
PCOD symptoms can vary from woman to woman, but common signs include:
- Irregular or missed menstrual periods
- Unwanted hair growth on the face and body
- Persistent acne
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Dark patches on the skin (especially around the neck and underarms)
- Mood swings or depression
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
Health Risks Associated with PCOD
If left untreated, PCOD can lead to several long-term health complications, such as:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypertension
- High cholesterol
- Endometrial cancer (due to prolonged absence of menstruation)
- Cardiovascular disease
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing PCOD involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests to check hormone levels, and ultrasound imaging to assess the ovaries.
Though there is no permanent cure for PCOD, its symptoms can be effectively managed through:
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management can significantly reduce symptoms.
- Medications: Hormonal birth control pills, insulin-sensitizing drugs like metformin, and anti-androgens may be prescribed.
- Stress management: Yoga, meditation, and other stress-relief techniques are beneficial.
Kindly visit Manipal TRUtest for hormonal testing and diagnostic packages tailored to women’s health. Early detection and appropriate medical care can help you manage PCOD effectively and lead a healthier life.
PCOD is more than just a reproductive disorder; it is a hormonal imbalance that affects multiple aspects of a woman's health. Early detection plays a crucial role in managing its effects, and undergoing a PCOD test can help identify hormonal irregularities before they lead to more serious complications. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and long-term implications, women can take charge of their health through timely medical care, lifestyle changes, and informed decisions. Awareness and proactive care are essential first steps toward restoring hormonal balance and overall well-being.
PCOD / PCOS
The Role of PCOD Test in Women’s Hormonal Health
Polycystic Ovary Disease (PCOD), also known as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), is a common hormonal disorder affecting millions of women worldwide, particularly those of reproductive age. It is also characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excessive androgen levels, and the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries. PCOD can disrupt various aspects of a woman’s health, including fertility, metabolism, and emotional well-being. Early diagnosis through PCOD testing plays a very crucial role in managing this condition effectively and safeguarding hormonal health.
Understanding PCOD and Its Impact
PCOD arises from an imbalance in the female hormones, primarily an excess of androgens (male hormones) that disrupt normal ovarian function. This hormonal imbalance leads to irregular or absent periods, making it difficult for women to conceive. Additionally, PCOD often causes symptoms such as unwanted facial and body hair growth, acne, weight gain, and hair thinning. Beyond reproductive issues, PCOD is associated with insulin resistance, which increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Given the complex nature of PCOD and its potential health complications, early and accurate diagnosis is essential. Without proper intervention, the condition may worsen over time, leading to long-term health challenges such as infertility, metabolic syndrome, and mental health disorders including anxiety and depression.
The Importance of PCOD Testing
PCOD testing involves a combination of clinical evaluation, hormonal assays, and imaging studies. Blood tests measure hormone levels including luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), testosterone, and insulin. These tests help to detect the characteristic hormonal imbalances of PCOD. Additionally, ultrasound imaging of the ovaries can reveal the presence of multiple cysts and assess ovarian size, which are key indicators in confirming the diagnosis.
These diagnostic tools allow healthcare providers to differentiate PCOD from other conditions with similar symptoms, such as thyroid disorders or adrenal gland abnormalities. Early detection through these tests enables personalized treatment plans tailored to the severity of the condition and individual health needs.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis and Management
Early diagnosis of PCOD through testing has several advantages. It allows for timely interventions that can regulate menstrual cycles, improve fertility outcomes, and manage symptoms like acne and excessive hair growth. Lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management are often recommended to improve insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to address specific symptoms or hormonal imbalances. Birth control pills, anti-androgens, and insulin-sensitizing drugs are commonly prescribed treatments. Ongoing monitoring through regular PCOD testing helps assess the effectiveness of these interventions and guide any necessary adjustments.
PCOD Testing and Holistic Health
Beyond reproductive health, PCOD testing plays a vital role in preventing associated metabolic and psychological complications. Since PCOD increases the risk of insulin resistance, diabetes, and heart disease, regular monitoring can help in early identification and prevention of these conditions. Moreover, recognizing the emotional and psychological impact of PCOD emphasizes the need for comprehensive care, including mental health support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PCOD testing is an indispensable part of women’s healthcare, offering insights into hormonal imbalances that affect not only fertility but overall well-being. Early and accurate diagnosis through hormone assays and ultrasound imaging empowers women to take control of their health with appropriate treatments and lifestyle changes. By prioritizing PCOD profile testing, women can better manage symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. Awareness and proactive care remain key to addressing the challenges posed by PCOD effectively.
